The Database Dictionary |
| This dictionary holds descriptions of tables and objects that have been created by users, the system and the database administrator. The dictionary is an internal and unique database that allows the operation of the databases created by the administrators. Este diccionario almacena la descripción de las tablas y los objetos que han sido creados por los usuarios, el sistema y el administrador de la base de datos. El diccionario es una base de datos interna y única que permite que operen las bases de datos creadas por los administradores. |
| Tip |
| The Data Dictionary contains many views and tables. The dictionary allows writing efficient and elegant PL/SQL code. Several books have been written to describe the organization of it. El diccionario contiene diversas vistas y tablas que permiten escribir código PL/SQL elegante y eficiente. Varios libros han sido escritos para describir la organización del diccionario de datos. |
| Tip |
In Oracle, the tables in the dictionary are prefixed so that their elements are easy to identify.
En Oracle las tablas del diccionario tienen los prefijos mostrados para ayudar a su identificación.
|
Constraints |
In Oracle the constraints are stored in the user_constraints table (all_constraints table, dba_constraints table) and the value of the column constraint_type are:
En Oracle las rectricciones están almacenadas en la tabla de user_constraints (en la tabla de all_constraints, en la tabla de dba_contraints) y el valor de la columna constraint_type puede ser de:
|
Microsoft SQL Server Dictionary |
In Microsoft SQL Server, database object information is stored in the tables sysobjects and sysdatabases (from the MASTER database). In the sysobjects table the xtype column indicates the object type as shown below:
En Microsoft SQL Server la información de los objetos se encuentra en las tablas sysobjects y sysdatabases (del la base de datos MASTER). En la tabla sysobjects la columna xtype indica el tipo de objeto como se muestra:
|
| Problem 1 |
| motorola > Write a SQL command in Oracle to display the name of the columns in the user_tables table in the motorola database. Escriba un comando SQL en Oracle para mostrar el nombre de las columnas en la tabla user_tables en la base de datos motorola. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| Name Null? Type ----------------------------------------- -------- ---------------- TABLE_NAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30) TABLESPACE_NAME VARCHAR2(30) CLUSTER_NAME VARCHAR2(30) IOT_NAME VARCHAR2(30) STATUS VARCHAR2(8) PCT_FREE NUMBER PCT_USED NUMBER INI_TRANS NUMBER MAX_TRANS NUMBER INITIAL_EXTENT NUMBER NEXT_EXTENT NUMBER MIN_EXTENTS NUMBER MAX_EXTENTS NUMBER PCT_INCREASE NUMBER FREELISTS NUMBER FREELIST_GROUPS NUMBER LOGGING VARCHAR2(3) BACKED_UP VARCHAR2(1) NUM_ROWS NUMBER BLOCKS NUMBER EMPTY_BLOCKS NUMBER AVG_SPACE NUMBER CHAIN_CNT NUMBER AVG_ROW_LEN NUMBER AVG_SPACE_FREELIST_BLOCKS NUMBER NUM_FREELIST_BLOCKS NUMBER DEGREE VARCHAR2(40) INSTANCES VARCHAR2(40) CACHE VARCHAR2(20) TABLE_LOCK VARCHAR2(8) SAMPLE_SIZE NUMBER LAST_ANALYZED DATE PARTITIONED VARCHAR2(3) IOT_TYPE VARCHAR2(12) TEMPORARY VARCHAR2(1) SECONDARY VARCHAR2(1) NESTED VARCHAR2(3) BUFFER_POOL VARCHAR2(7) FLASH_CACHE VARCHAR2(7) CELL_FLASH_CACHE VARCHAR2(7) ROW_MOVEMENT VARCHAR2(8) GLOBAL_STATS VARCHAR2(3) USER_STATS VARCHAR2(3) DURATION VARCHAR2(15) SKIP_CORRUPT VARCHAR2(8) MONITORING VARCHAR2(3) CLUSTER_OWNER VARCHAR2(30) DEPENDENCIES VARCHAR2(8) COMPRESSION VARCHAR2(8) COMPRESS_FOR VARCHAR2(12) DROPPED VARCHAR2(3) READ_ONLY VARCHAR2(3) SEGMENT_CREATED VARCHAR2(3) RESULT_CACHE VARCHAR2(7) |
| Problem 2 |
| motorola > Write a SQL command in Oracle to display the name of all the tables in the motorola database. Escriba un comando SQL en Oracle para mostrar el nombre de todas las tablas en la base de datos motorola. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| DEPT EMP DEMO_USERS DEMO_CUSTOMERS DEMO_ORDERS DEMO_PRODUCT_INFO DEMO_ORDER_ITEMS DEMO_STATES APEX$_ACL APEX$_WS_WEBPG_SECTIONS APEX$_WS_ROWS APEX$_WS_HISTORY APEX$_WS_NOTES APEX$_WS_LINKS APEX$_WS_TAGS APEX$_WS_FILES APEX$_WS_WEBPG_SECTION_HISTORY DEPARTMENT EMPLOYEE SKILL EMP_SKILL |
| Problem 3 |
| motorola > Write a SQL command in Oracle to display the name of all the tables in the motorola database that their names do not start with DEMO_ neither APEX$_. Escriba un comando SQL en Oracle para mostrar el nombre de todas las tablas en la base de datos motorola que sus nombres no empiezan con DEMO_ ni con APEX$_. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT table_name, tablespace_name ... TABLE_NAME TABLESPACE_NAME ------------------------------ ------------------------------ DEPARTMENT USERS DEPT USERS EMP USERS EMPLOYEE USERS EMP_SKILL USERS SKILL USERS 6 rows selected. |
| Problem 4 |
| city_bank > Write a SQL command in Microsoft SQL Server to list the name of the tables in the city_bank database. Escriba un comando SQL en Microsoft SQL Server para lista el nombre de las tablas en la base de datos de city_bank. |
| mot_server.sql |
| USE city_bank; SELECT ... FROM sysobject ... |
| Problem 5 |
| city_bank > Write a SQL command in Oracle to list the name of the stored procedures. Use the user_procedures table. Escriba un comando SQL en Oracle para lista el nombre de los procedimientos almacenados. Use la tabla user_procedures. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT ... P_CONCAT P_MONTHLY P_CELSIUS P_LITERS P_DUPLICATE P_COMCAT P_TWOINPUTS P_NUMPUT P_NUMERIC P_ABOUTME P_HELLO P_RECLIST P_LISTCLIENT TAX P_TAX IMPUESTO P_BALAN CUSTOM_AUTH CUSTOM_HASH APEX$_WS_FILES_T1 UPDATE_ORDER_TOTAL INSERT_DEMO_PROD INSERT_DEMO_ORDER_ITEMS APEX$_WS_TAGS_T1 APEX$_WS_WEBPG_SECTIONS_T1 DEMO_USERS_T1 DEMO_ORDER_ITEMS_GET_PRICE APEX$_WS_NOTES_T1 APEX$_WS_ROWS_T1 APEX$_WS_LINKS_T1 BI_DEMO_USERS APEX$_ACL_T1 INSERT_DEMO_CUST 33 rows selected. |
| Problem 6 |
| city_bank > Repeat the previous problem removing those procedures that include the word DEMO_ or APEX$_ in their names using Oracle. Repita el problema anterior removiendo aquellos procedimientos que incluyan la palabra DEMO_ o APEX$_ en sus nombres usando Oracle. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT ... OBJECT_NAME ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- TAX P_TWOINPUTS P_TAX P_RECLIST P_NUMPUT P_NUMERIC P_MONTHLY P_LITERS P_LISTCLIENT P_HELLO P_DUPLICATE P_CONCAT P_COMCAT P_CELSIUS P_BALAN P_ABOUTME IMPUESTO CUSTOM_HASH CUSTOM_AUTH UPDATE_ORDER_TOTAL 20 rows selected. |
| Problem 7 |
| city_bank > Write a SQL command to list the stored procedures and functions in the database using Microsoft SQL Server. Cree un comando de SQL para listar todos los procedimientos y funciones en la base de datos usando Microsoft SQL Server. |

| Problem 8 |
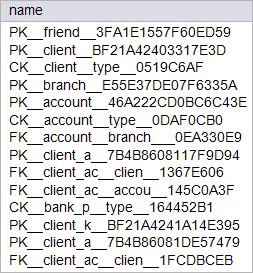
| city_bank > Write a SQL command in Oracle to list the name of PRIMARY KEY constraints that start with SYS_ in the database. Escriba un comando SQL en Oracle para lista el nombre de las restricciones del tipo de LLAVE PRIMARIA que empiezan con SYS_ en la base de datos. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT ... CONSTRAINT_NAME TABLE_NAME ------------------------------ ------------------------------ SYS_C007279 DEPT SYS_C007281 EMP SYS_C008939 FRIEND SYS_C008944 CLIENT SYS_C008949 BRANCH SYS_C008954 ACCOUNT SYS_C008956 CLIENT_ACCOUNT SYS_C008975 CLIENT_K SYS_C008976 CLIENT_ACCOUNT_K 9 rows selected. |
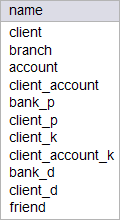
| Problem 9 |
| city_bank > Write a SQL command in Microsoft SQL Server to list the name of all the constraints in the database. Escriba un comando SQL en Microsoft SQL Server para lista el nombre de todas las restricciones en la base de datos. |
| Problem 10 |
| master > Write a SQL command using Microsoft SQL Server to list the name of all the databases (use the sysdatabases table). Escriba un comando SQL usando Microsoft SQL Server para listar el nombre de todas las bases de datos (use la tabla sysdatabases.) |

| Problem 11 |
| master > Write a stored procedure called p_existkim using Microsoft SQL server to indicate if the kimberly database exists. If it exists, then the procedure must list the names of the user and system tables in the master database. Escriba un procedimiento almacenado llamado p_existkim en Microsoft SQL Server que indique si existe la base de datos de kimberly. Si existe la base de datos, entonces el procedimiento lista las tablas de usuario y de sistema de la base de datos master. |
| SQL |
| USE master; EXECUTE p_existkim |
| Output |
| The kimberly database does exist SYST sysrowsetcolumn SYST sysrowsets SYST sysallocunits SYST sysfiles1 SYST syshobtcolumns SYST syshobts SYST sysftinds SYST sysserefs SYST sysowners SYST sysdbreg SYST sysprivs SYST sysschobjs SYST syslogshippers SYST syscolpars SYST sysxlgns SYST sysxsrvs SYST sysnsobjs SYST sysusermsgs SYST syscerts SYST sysrmtlgns SYST syslnklgns SYST sysxprops SYST sysscalartypes SYST systypedsubobjs SYST sysidxstats SYST sysiscols SYST sysendpts SYST syswebmethods SYST sysbinobjs SYST sysobjvalues SYST sysclsobjs SYST sysrowsetrefs SYST sysremsvcbinds SYST sysxmitqueue SYST sysrts SYST sysconvgroup SYST sysdesend SYST sysdercv SYST syssingleobjref SYST sysmultiobjrefs SYST sysdbfiles SYST sysguidrefs SYST syschildinsts SYST sysqnames SYST sysxmlcomponent SYST sysxmlfacet SYST sysxmlplacement SYST sysobjkeycrypts SYST sysasymkeys SYST syssqlguides SYST sysbinsubobjs USER spt_fallback_db USER spt_fallback_de USER spt_fallback_us USER MSreplication_o USER spt_monitor USER spt_values |
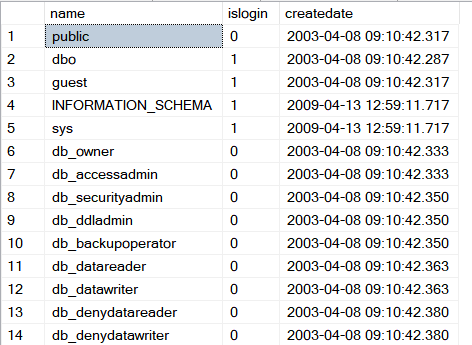
| Problem 12 |
| circuit_city > Test the following SQL statement to list the users in Microsoft SQL Server. Pruebe el siguiente comando de SQL para listar los usuarios en Microsoft SQL Server |
| SQL |
| SELECT name, islogin, createdate FROM sysusers; |
| Problem 12 |
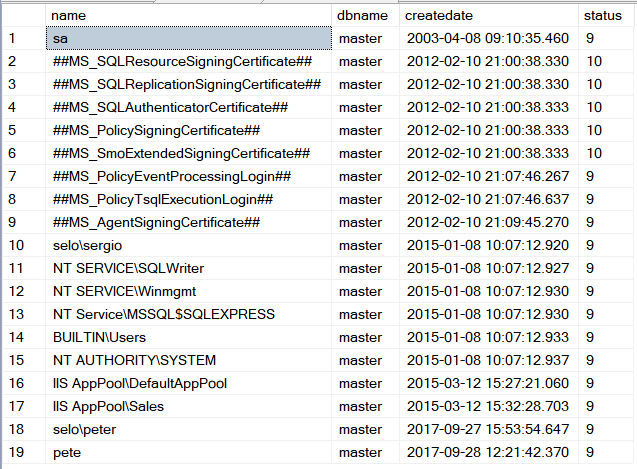
| circuit_city > Test the following SQL statement to list the LOGINS in Microsoft SQL Server. Pruebe el siguiente comando de SQL para listar los LOGINS en Microsoft SQL Server |
| SQL |
| SELECT name, dbname, createdate, status FROM syslogins; |